| ER stress 와 Diabetes |
|
이인규
경북의대 |
|
Eukaryotic cell에 있어서 Endoplasmic reticulum(ER)은 protein의 synthesis 와 modification. lipid biosynthesis, intracellular Ca2+ 의 항상성 유지 등에 중요한 역할을 한다. 이러한 기능들 중 에서도 protein의 synthesis 와 modification은 ER의 항상성이 유지되지 않을 때 (예: glycosylation의 변화, Ca2+ 고갈, mRNA translation의 증가, oxidative stress, energy deprivation, inflammation 등..) 쉽게 타격을 받게 되는데, 항상성이 깨어지면서 misfolded 혹은 unfolded protein이 ER내에 축적되는 상태를 ER stress라고 한다. ER stress가 발생하게 되면, 세포는 항상성을 유지하기 위한 intracellular signaling pathway를 활성화 시키게 되고 (이를 Unfolded protein response (UPR) 혹은 ER stress response 이라고 함), 크게 다음과 같은 네 가지의 반응이 일어난다. 첫 번째로 ribosome에서 mRNA로부터 protein으로 translation되는 것을 억제시킴으로써 ER내로 protein의 유입을 감소시키고, 두 번째로 protein folding에 필요한 ER chaperon의 mRNA expression을 증가 시켜 folding 능력을 향상 시킨다. 세번째 반응은 ER stress-associated degradation (ERAD)로 misfolded 혹은 unfolded protein을 분해하여 제거하는 과정이다. 이상의 ER stress response로 세포가 ER stress를 극복하지 못하면 apoptosis pathway가 활성화된다. 이들 반응에서 중요한 역할을 하는 ER membrane protein은 ATF6(Activating transcription factor 6), IRE1(Inositol requiring protein 1), 그리고 PERK (Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase) 으로 알려져 있다 (그림 1). 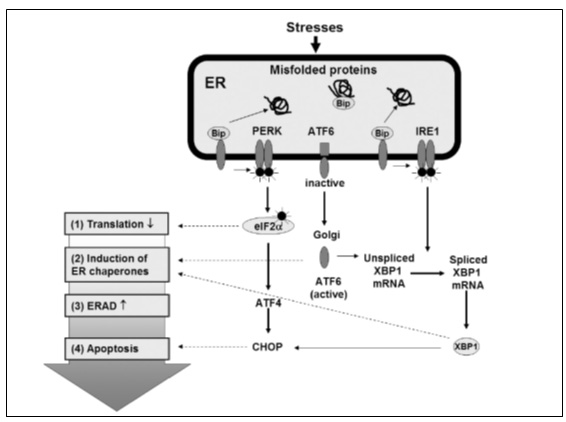 그림 1. ER stress에 의한 신호전달 최근 10년 동안의 임상 및 전임상 연구들을 보면, ER stress 와 ER stress response가 insulin resistance, diabetes, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, atherosclerosis와 같은 다양한 대사 질환들과 연관이 있음을 제시하고 있으며 (그림 2), 이글에서는 이들 중에서 당뇨병과의 연관성에 대하여 알아 보고자 한다. 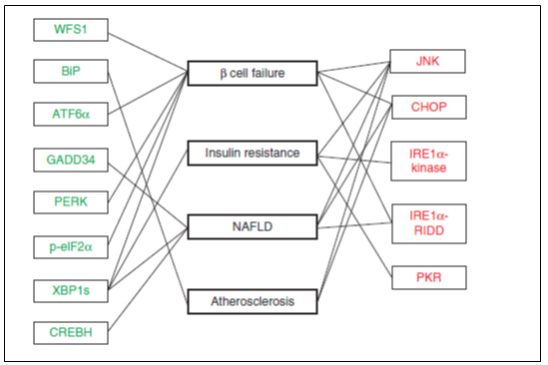 그림 2. ER stress response 관련 인자들과 대사성 질환의 관계 Insulin과 같은 secretory protein의 합성과 분비가 활발하게 이루어지는 췌장의 β-cell 에는 ER이 발달되어 있으며, 중요한 역할을 하는 것으로 잘 알려져 있다. Preproinsulin은 ER에서 posttranslational modification의 과정을 통해 disulfide bond를 이룬 proinsulin으로 바뀌고 c-peptide가 분리되어 활성형 insulin이 되는데, insulin resistance가 발생하거나 hyperglycemia가 지속되면, 이를 극복하기 위해 insulin의 합성과 분비가 증가하게 되고, 적정 수준을 넘게 되면 ER stress를 초래할 수 있다. 이런 특징 때문에 ER의 원활한 기능이 β-cell의 기능 유지에 중요한 역할을 하고, ER stress에 의한 β-cell기능 이상은 당뇨병을 유발할 것으로 생각되어 많은 연구들이 이루어지고 있다. ER stress responsive molecule들과 insulin synthesis, gluconeogenesis, insulin resistance 및 pancreatic β-cell apoptosis와의 관계에 대하여 알아봄으로써 ER stress의 관점에서 당뇨병의 pathogenic mechanism을 이해하고, 나아가 새로운 치료 전략에 대하여서도 알아보고자 한다. <참고 문헌>
|